Domain I: CPMAI AI Fundamentals provides the essential groundwork for understanding the principles and potential of Artificial Intelligence in project environments. This domain equips professionals with the foundational knowledge needed to effectively evaluate, plan, and guide AI-driven projects within their organizations.
Through this domain, learners gain a clear understanding of how AI differs from traditional software approaches, why data is central to AI success, and how AI technologies such as machine learning can be applied to solve real-world problems. This knowledge is critical for project leaders who must bridge the gap between technical teams and business stakeholders.
What You’ll Learn in Domain I: AI Fundamentals
This section of the course provides a comprehensive foundation in AI, machine learning (ML), and deep learning. You will explore core AI principles, the evolution of AI technologies, and their increasing relevance in business and project environments. This includes a focused overview of Generative AI—covering its terminology, applications, and strategies—and a deep dive into various learning methods such as:
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
These concepts are tied directly to the real-world execution of AI projects, helping participants understand how these learning methods can be aligned with specific business needs.
Subscribe for the course here: pmi.org/shop/tc/p-/digital-product/cognitive-project-management-in-ai-(cpmai)-v7—training-,-a-,-certification/cpmai-b-01
Access course here: learning.pmi.org
You should master the first sections of the CPMAI course content, aligned with Domain I: AI Fundamentals. This part sets the stage for learners to gain a strong foundation in artificial intelligence, its core concepts, and practical uses:
CPMAI Introduction & Welcome
This opening module orients learners to the CPMAI (Cognitive Project Management in AI) framework. It provides an overview of the course structure, learning objectives, and certification goals. You’ll gain insight into how the CPMAI methodology uniquely bridges the gap between project management best practices and AI development needs. This session also emphasizes the importance of applying a structured, iterative methodology to successfully lead AI initiatives.
Module 1. What is Artificial Intelligence?
In this foundational lesson, you will:
- Define artificial intelligence and distinguish it from human intelligence.
- Understand AI’s core components: machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics.
- Learn about the different types of AI: Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), Strong AI, Weak AI, and Narrow AI.
- Explore how AI systems “think,” evaluate their capabilities, and understand the significance of the Turing Test.
This module demystifies AI, helping learners build a clear mental model of what AI is—and isn’t.
Module 2. Applications of AI
This section introduces learners to real-world use cases and practical applications of AI across industries, including finance, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, and logistics. It also:
- Explores the seven patterns of AI (e.g., recognition, conversation, prediction, goal-driven systems).
- Teaches how to identify when and where AI is appropriate—and when it is not.
- Helps participants evaluate AI solutions based on business needs, feasibility, and value potential.
Together, these introductory modules form the basis of Domain I: AI Fundamentals, equipping learners with the context and clarity needed to move forward confidently through the rest of the CPMAI course.
Domain I includes three key tasks:
Task 1: Understanding of AI Fundamentals and Evolution
To effectively lead AI initiatives, project professionals must first build a strong foundation in what Artificial Intelligence (AI) truly is—and what it is not. Task 1: Understanding of AI Fundamentals and Evolution is designed to help you gain a comprehensive understanding of the core concepts, historical context, and current significance of AI. This knowledge enables informed decision-making and responsible leadership in AI-driven projects.
At its core, AI is the science of building systems that mimic aspects of human intelligence. In this task, you’ll define AI in practical terms and explore how it compares to and interacts with natural human intelligence. You’ll delve into the distinctions between Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), Strong AI, Weak AI, and Narrow AI, understanding the realistic boundaries of today’s technology and where it’s heading.
One of the key concepts introduced is the Turing Test, a foundational idea in AI evaluation that assesses a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behavior indistinguishable from that of a human. You’ll examine the significance and limitations of this test and explore its implications for modern AI systems.
The task also introduces cognitive computing, a field that overlaps with AI but emphasizes human-like reasoning and interaction. You’ll learn how cognitive computing is being used in real-world applications such as customer support, document analysis, and decision-making systems.
A crucial part of this task is separating fact from fiction. With so much hype surrounding AI, it’s easy to fall prey to myths and misconceptions. This section helps you understand what AI can realistically do today—and what remains in the realm of science fiction.
You’ll also explore augmented intelligence, a concept that focuses on AI as a tool to enhance human decision-making rather than replace it. This shift in perspective is vital for successfully applying AI to solve practical business problems.
Understanding AI also requires historical context. You’ll trace the evolution of AI, including key milestones, the rise and fall of early optimism, and the periods of stagnation known as AI winters. These lessons from history are essential for setting realistic expectations and avoiding past mistakes.
You’ll gain familiarity with early AI methods such as symbolic systems, expert systems, and fuzzy logic, learning how these approaches laid the groundwork for today’s more data-driven AI techniques.
Finally, this task helps you understand why AI is thriving today—from advances in computing power and data availability to the growing demands of digital transformation. You’ll explore how AI aligns with broader organizational shifts and how it can be leveraged to address modern business challenges.
By the end of this task, you’ll have a clear, realistic, and strategic understanding of AI’s fundamentals and its evolution—positioning you to engage confidently with stakeholders and steer your projects toward success.
Task 2: Evaluating AI Applications and Patterns
The true power of AI lies in its ability to solve real-world problems—but only when applied correctly. Task 2: Evaluating AI Applications and Patterns equips project professionals with the insights needed to identify when, where, and how to apply AI solutions effectively within their organizations.
This task begins by teaching you how to identify appropriate AI use cases. You’ll learn how to analyze business challenges and determine which problems are best addressed with AI or cognitive technologies. From optimizing workflows to enhancing customer experiences, this task helps you match capabilities to needs for maximum impact.
Just as important as knowing where to use AI is understanding its limitations. You’ll explore scenarios where AI might not be suitable—whether due to lack of data, ethical constraints, explainability requirements, or business complexity. This critical thinking prevents wasteful investment and promotes responsible AI adoption.
A central concept introduced in this task is the seven patterns of AI, which serve as a framework for categorizing and implementing AI solutions. These include:
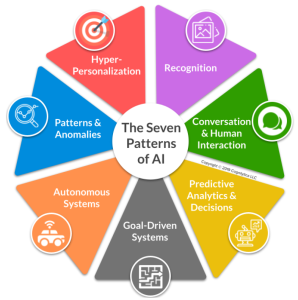
- Recognition (such as image or voice detection),
- Conversation & Human Interaction (including chatbots and virtual assistants),
- Predictive Analytics &Decisions (like forecasting outcomes),
- Goal-Driven Systems (AI that takes action to achieve a goal),
- Autonomous Systems (such as self-driving cars),
- Patterns & Anomalies (identifying unusual patterns),
- Hyper-Personalization (tailoring experiences to users).
You’ll learn how to apply these patterns to real business challenges, either individually or in combination, to create powerful and flexible AI-driven applications.
One focus area within this task is conversational AI. You’ll explore how to implement natural language processing (NLP) and AI-based communication tools like chatbots, voice assistants, and virtual agents. Understanding technologies like speech recognition, text-to-speech, and machine translation will enable you to deploy multilingual and accessible AI solutions that expand your organization’s reach.
In addition, the task covers pattern and anomaly detection, helping you leverage AI to discover insights hidden in large volumes of data—vital for use cases like fraud detection, equipment maintenance, and quality control.
A distinction is also made between AI and robotic process automation (RPA), including the differences between attended bots (which assist humans) and unattended bots (which work independently). Understanding when to use RPA versus AI ensures that automation projects are scoped and executed correctly.
Finally, this task introduces you to goal-driven AI systems—models that don’t just provide insights, but also take actions to meet objectives. You’ll also learn how to integrate multiple AI patterns within a single solution for more comprehensive capabilities, combining, for example, prediction with conversation to build intelligent customer support platforms.
By completing this task, you’ll gain the ability to critically evaluate AI opportunities, design tailored AI strategies, and align them with organizational goals—ensuring that your projects are not only technically feasible but also practically valuable.
Task 3: Applying Machine Learning Fundamentals
Machine learning (ML) is the engine that powers most modern AI solutions. Task 3: Applying Machine Learning Fundamentals introduces project professionals to the essential concepts, methodologies, and techniques needed to understand and apply machine learning in real-world projects.
This task begins by clarifying what machine learning is and why it serves as the cornerstone of AI today. You’ll learn how ML systems enable AI to learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed. This foundational understanding is crucial for managing AI projects, even if you’re not the one building the algorithms.
One of the first distinctions covered is between probabilistic and deterministic approaches. Probabilistic methods make decisions based on likelihood and uncertainty—ideal for complex, data-rich environments. Deterministic methods follow fixed rules and logic. Understanding when to apply each helps in designing the right type of AI system.
You’ll also compare heuristic techniques (which use shortcuts or rules of thumb to solve problems efficiently) to brute-force search methods, which systematically evaluate all possibilities. This comparison is especially relevant for optimization tasks and algorithm selection.
This task also helps you understand the differences between prediction, inference, and generalization—three pillars of ML performance. You’ll discover how to evaluate whether a model merely memorizes data or truly learns patterns that can apply to unseen cases.
Understanding the difference between machine learning algorithms and models is key. Algorithms are the step-by-step procedures used to train a model, while the model itself is the output of that training. You’ll gain clarity on how to choose and manage both during the project lifecycle.
Crucially, this task explores the three main types of machine learning:
- Supervised learning, where the model learns from labeled data,
- Unsupervised learning, where the model identifies patterns in unlabeled data,
- Reinforcement learning, where the model learns through trial and error based on feedback from its environment.
You’ll learn when and how to apply each type to solve specific business problems.
Machine learning also involves dealing with high-dimensional data, which can introduce complexity. You’ll learn strategies for addressing dimensionality challenges, such as the “curse of dimensionality,” which can impair model performance. This leads naturally to a discussion of feature engineering (the process of selecting and crafting meaningful input variables) and feature reduction (minimizing the number of variables to improve model efficiency and accuracy).
Finally, for projects that involve text data, this task introduces tokenization and vectorization—the processes by which raw language data is broken into units and transformed into numerical representations. These techniques are essential for building AI systems that understand or generate human language, such as chatbots or recommendation engines.
By mastering the material in this task, you will develop a robust foundation in machine learning—enabling you to collaborate more effectively with data scientists, make informed project decisions, and ensure that your AI initiatives are built on strong, data-driven principles.
Test Your Knowledge
This domain ensures that CPMAI-certified professionals are not only conversant in AI terminology but also capable of leading AI initiatives with clarity and strategic insight.
To complete this domain, take a micro-exam to assess your understanding.
You can start the exam by using the floating window on the right side of your desktop screen or the grey bar at the top of your mobile screen.
Alternatively, you can access the exam via the My Exams page: 👉 KnowledgeMap.pm/exams
Look for the exam with the same number and name as the current PMI CPMAI ECO Task.
After completing the exam, review your overall score for the task on the Knowledge Map: 👉 KnowledgeMap.pm/map
To be fully prepared for the actual exam, your score should fall within the green zone or higher, which indicates a minimum of 70%. However, aiming for at least 75% is recommended to strengthen your knowledge, boost your confidence, and improve your chances of success.
